このページはコレクションパイプラインパターンの操作について説明します。詳細については
- コレクションパイプラインの記事をご覧ください。コレクションパイプラインパターンの説明を含む記事です。
- 操作カタログ。これらページで扱う、選択した操作のリストです。
flat-map
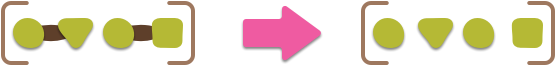
コレクションに機能をマップし、結果を 1 レベル分フラッテンします。
リストに対する関数をマップして、関数がリストで複数の値を返すことはよくありますが、出力が入力と同様にネストされることを望まない場合があります。
Ruby…
["two birds", "three green peas"].
flat_map {|s| s.split}
# => ["two", "birds", "three", "green", "peas"]
Clojure…
(mapcat #(clojure.string/split % #"\s+")
["two birds" "three green peas"])
;; => ("two" "birds" "three" "green" "peas")
論理的には、map とその後に 1 レベルの flatten を実行したものと同じです。
Ruby…["two birds", "three green peas"].
map {|s| s.split}.
flatten (1)
# => ["two", "birds", "three", "green", "peas"]
ただし、非常に多くのプラットフォームが flat-map 操作を提供しているため、非常に一般的に使用されています。
また、map の結果をすべて取得し、結果を連結するのと同じと考えることもできます。したがって、Clojure の名前は「mapcat」です。
Clojure…(apply concat (map #(clojure.string/split % #"\s+")
["two birds" "three green peas"]))
;; => ("two" "birds" "three" "green" "peas")
